When babies swallow them, the spores can turn into growing, multiplying bacteria that pump out a poison called botulinus toxin (or botulinum toxin). Botulism is a rare but serious illness caused by a toxin that attacks the body’s nerves.

What Is Infant Botulism How Is It Treated Causes Symptoms Prevention Of Infant Botulism
Babies’ intestines are an ideal environment for the spores.

What is environmental infant botulism. Honey is a recognised cause of infant botulism, hence recommendations to avoid honey before the age of. You can help reduce the risk of this disease by only feeding honey to healthy children over one year of age. Infant botulism by the government of canada.
The disease results after spores of the bacterium clostridium botulinum or related species are swallowed, temporarily colonize an infant’s large intestine, and produce botulinum neurotoxin. Epidemiologic and laboratory investigations of this recently recognized disease were undertaken to identify risk factors and routes by which c. Bacteria from the spores can grow and multiply in a baby’s intestines, producing a.
A loss of appetite may be apparent, as the baby may refuse to eat or nurse. Infant botulism could be a life threatening disease that produces toxins inside the body and causes breathlessness in babies. Infant botulism results from the in vivo production of toxin by clostridium botulinum after it has colonized the infant's gut.
Botulinum) spores causes this illness. Many babies will appear sluggish and lack a normal level of energy. Infant botulism is most commonly caused by ingestion of bacteria spores from the environment and sometimes from ingestion of honey.
Botulinum spores contaminate a wound and produce toxin. Botulinum spores might reach susceptible infants. Honey and other environmental risk factors for infant botulism woden a c t environmental health branch.
Department of health type a, and treatment with guanidine. The individual beekeeper should be prepared to answer questions responsibly about infant botulism and honey. This toxin is absorbed through their immature intestines and causes infant botulism.
Botulinum spores germinate and produce toxin in the gastrointestinal tract of infants. Botulinum for the most cases remain unclear. Ingestion of spores leads to toxin.
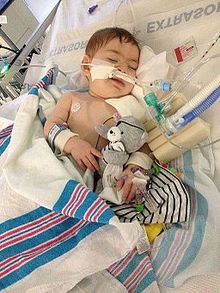
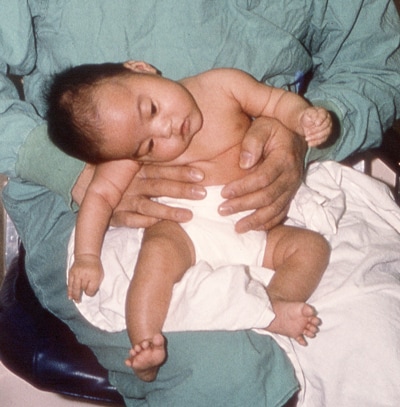
Though infant botulism is a severe condition, it can be treated if detected early. Infant botulism is an intestinal toxemia. Symptoms of botulism usually start with weakness of the muscles that control the eyes, face, mouth, and throat.
Some cases of infant botulism are mild, but some are fatal. Constipation is generally one of the first symptoms of infant botulism. The risk factors and vehicles of transmission of c.
Food and drug administration for the treatment. Infant botulism is a rare illness that can happen when a baby ingests bacteria that produce a toxin inside the body. Furthermore, clostridium botulinum is not a disease of the honey bee, but rather the spores are a rare accidental contaminant carried into the hive on dust, water, or pollen from the environment.
Infant botulism occurs when c. A n n neuro/t979 addendum since. In infant botulism, the biology is different because the toxin forms only after ingestion of bacterial spores which germinate in the gut and then release toxin.
Botulism in infants under one year of age has been associated with ingestion of c. In canada, honey is the only food that has been linked to infant botulism. Always watch for symptoms of infant botulism in babies and start treatment as soon as infant botulism is diagnosed.
Botulinum spores from the environment or specific foods such as honey. First recognized in 1976, infant botulism occurs globally and is the most common form of human botulism in the united states. This weakness may spread to the neck, arms, torso, and legs.
Infant botulism is a rare but serious form of food poisoning that can affect babies up to a year old. Infants may show signs of weakness, which can include weak cries. Exposure to clostridium botulinum (c.
When and for how long is a person able to spread the disease? Wound botulism occurs when c. The neurotoxin binds to cholinergic nerve terminals and cleaves intracellular proteins necessary for acetylcholine release, resulting.
Botulism - Wikipedia

References In Infantile Botulism Clinical Manifestations Treatment And The Role Of The Nurse Practitioner - The Journal For Nurse Practitioners

Pdf Infant Botulism

Botulism In Babies Baby Dies After Family Feeds Him Honey

Pdf Infant Botulism With Prolonged Faecal Excretion Of Botulinum Neurotoxin And Clostridium Botulinum For 7 Months

Laboratory-confirmed Infant Botulism In Canada Summary Of Surveillance Morbidity And Microbiology 19792019 Ccdr 4778 - Canadaca

Babies Honey And Botulism Microbiology
Toxins Free Full-text Public Health Risk Associated With Botulism As Foodborne Zoonoses Html

Descriptive Epidemiology Of Infant Botulism In California The First 40 Years - The Journal Of Pediatrics
Infant Botulism Information For Clinicians Botulism Cdc

Infant Botulism What You Need To Know Safe Healthy Food For Your Family

Laboratory Diagnostics Of Botulism The Standard Methods Are Marked Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf Infant Botulism Semantic Scholar

Environmental Samples Collected From California Infant Botulism Download Table

Foodborne Botulism Or Please Dont Pass The Olives

Botulism Presented By Hosam Hassan Under Supervision Of

Jkms Journal Of Korean Medical Science

Infant Botulism Diagnosis Treatment And Prevention Via Drgreenecom

Pdf Infant Botulism Semantic Scholar
